Imagine you’ve spent countless hours designing and developing a stunning application that perfectly serves your users’ needs. Now, imagine discovering a data breach that exposes sensitive user information to cybercriminals, causing irreparable damage to your reputation and users’ trust. A terrifying thought, isn’t it?
In today’s digital age, securing applications is no longer an option but an absolute necessity, especially when it comes to the seemingly invisible threads that connect your applications—the integrations and data transits. But let’s face it; amidst the rush to roll out impressive applications, security considerations often end up in the backseat, until a costly breach brings them into the spotlight.
That’s why we’re introducing MuleSoft Flex Gateway, a game-changing solution designed to fortify your applications, making data security an integral part of their DNA, rather than an afterthought. Ready to delve deeper into this world of secure data transit? Let’s uncover the wonders of Flex Gateway together.
What is Flex Gateway
Anypoint Flex Gateway is MuleSoft’s new ultra-fast API gateway designed to manage and secure APIs running anywhere. The gateway is built to deliver the performance required for the most demanding applications while providing enterprise-grade security and management.
Flex Gateway was designed to manage and secure APIs running anywhere, in your data centre or cloud of preference. It is the newest component in the quest of Universal API Management across both Mule and non-Mule APIs.
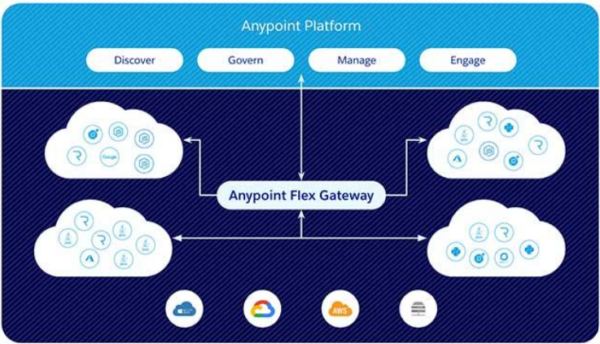
Flex Gateway vs. Mule Gateway
Typically, organizations have data across multiple systems and technologies, which results in a diverse set of APIs that can be challenging to manage. Before the introduction of Anypoint Flex Gateway, non-Mule APIs had to be managed differently from Mule applications — while you could discover, manage, and monitor any API there was a requirement to run a proxy Mule application to accomplish this, which results in lost efficiency.
Flex Gateway was designed to bridge the gap between securing both Mule APIs and non Mule APIs. Most organizations have APIs built with different technologies which makes it hard to manage from a security perspective, also difficult to discover and govern. Flex Gateway has come to fill the void when it comes to managing all your APIs, enabling you to have a piece of mind knowing your APIs will be managed consistently in a single platform, protected with world-class API security.
Licensing
A Mulesoft Anypoint API Management license is required to use Flex Gateway (Flex Gateway can be purchased individually, however may be restricted to local mode only and will need to manage as code locally via CLI or this can be automated with a CI/CD pipeline); cost is measured by volume of API requests, APIs managed and APIs governed.
Use Case for Flex Gateway
You have several APIs built with different technologies running in different environments, often this would involve having completely different security implementations, which can be hard to maintain and track.
Flex Gateway will provide powerful security to your applications anywhere, while giving you the power to have Flex Gateway on the same network, bolstering performance and reducing painful latency. Making security a deserved requirement for your APIs while remaining ultra fast.
Benefits of using Flex Gateway:
- Maintain proxies for all APIs in one place
- Apply security policies to all your APIs with ease
- Ability to scale up/out Flex Gateway instances to improve performance
- Ability to use CI/CD to maintain your configuration
Faster latency when Flex Gateway is on the same network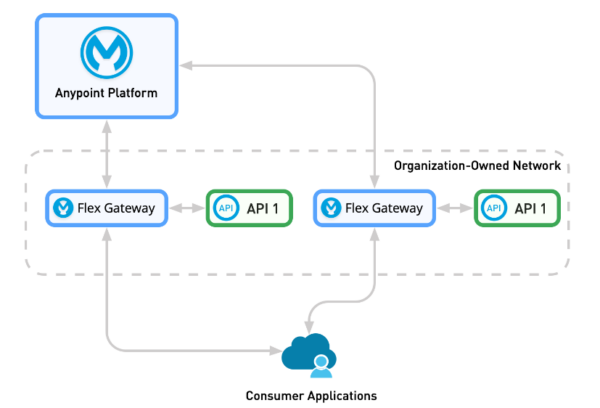
Figure 2: Use case of Flex Gateway supporting non-Mule APIs
Taking a deep dive into Flex Gateway’s capabilities
Replicas
With replicas you can scale out Flex Gateway to serve even more traffic and improve its performance and resilience. Replicas are their own instances of Flex Gateway that each sit in its own container running on Docker or Kubernetes for example. It is a good idea to deploy Flex Gateway as a cluster that enables multiple replicas to run in parallel. Replicas can also be scaled up vertically by increasing CPU and memory performance or horizontally by having multiple Replicas for load balancing or high availability. For high throughput, either choose more replicas with lower CPU performance allocation or choose fewer replicas with higher CPU performance allocation.
TLS Context
Secure your APIs by requiring Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption policies on your ingress/egress traffic. You have the option of using different ciphers to provide encryption methods. Flex gateway supports the following ways of encrypting your data:
- TLS between client and API (inbound TLS)
- TLS between API and upstream service (outbound TLS)
- Mutual authentication TLS (mTLS) in both inbound/outbound directions
TLS Context is applied through the port instead of the API instance; this means that any API that shares the same port will have TLS encryption applied to its traffic.
Shared Storage
Enable shared storage to use distributed caching and rate-limiting policies. To activate Shared Storage, changes need to be made to a custom YAML configuration file. It is recommended that a third party service such as Redis is used. If Redis is not defined, shared storage services are still available via port 4000 but will use an in-memory implementation instead.
Forward Proxy
A Forward Proxy requires all external traffic to be routed through a proxy connection. All upstream/downstream communication must pass through the proxy, this enables you to hide connection details of your API and instead use the endpoint connection provided in Flex Gateway.
Although Flex Gateway doesn’t have its own Forward Proxy, services such as Squid can be setup instead via updating a YAML configuration file. The noProxy Parameter can be used in the YAML configuration file to exclude traffic to and from certain APIs.
Liveness Check
This provides functionality that can be used to test the health of your gateway to ensure it is operating as expected. The Liveness check can be run from the CLI, this can be called manually or by setting up an automated script to verify that the Flex Gateway is running normally. If Flex Gateway is deployed in Kubernetes, then this will probe Flex Gateway automatically.
PROXY Protocol
Generally, when a request passes through a proxy or a load balancer, everything regarding where the message came from is striped and replaced by the proxy’ or load balancers’ own information. This might be problematic with some systems that depend on specific information about the sender such as the source IP address. Having a forward proxy implemented will satisfy any requirements where all sender information is retained such as an IP address.
PROXY Protocol is enabled as a Linux Service, a YAML file needs to be created and stored in the Flex Gateway configuration directory.
Caching
Make APIs even faster by enabling caching on them. By using a cache, it is possible to make your API respond faster. Caching stores commonly requested information in local memory on the Flex Gateway instance instead of making a new request every time, leading to lower latency. With caching, it is recommended to test your APIs extensively to ensure they behave as expected. Caching is applied to the API individually and not as a blanket approach. Configure Caching for an API by adding a caching policy to it. Requires Shared Storage to be set up.
Logging
Logging can be used to monitor your API traffic and can be useful for debugging any issues. Logs can be viewed from the Anypoint API Manager or log files on the local machine by adding the logging policy to that API. Logs can also be sent to any third-party platform that supports any Fluent Bit output type. To activate logging, Flex Gateway can be configured to output runtime and access logs.

CI/CD Capabilities
Flex Gateway can be configured using a CI/CD platform to automate the deployment of configuration files, add new APIs and configure policies. These capabilities enable consistent code reuse, allowing you to build the Flex Gateway in the same manner repeatedly. They also provide the necessary tools to configure APIs, ensuring that changes are verified and meet the required criteria, including auditing. Using a pipeline allows you to manage your configuration files in source control repository system, where you can effectively track and monitor any modifications made to them.
Security policies
Security policies are of upmost importance when it comes to securing your API, they are applied to APIs individually. There are multiple out-of-the-box polices that can be used with minimal fuss, however, do note that there is a balance when configuring security policies; having too many set up at once will slow down your API due to the increased load on resources.
- Basic Authentication – Use simple or LDAP authentication that requires a username and password
- Header Injection/Removal – Add and remove headers to/from requests or responses
- IP Allowlist/Blocklist – Configure to only allow a short list of IP addresses or block certain IP addresses
- JSON Threat Protection – Provides protection from malicious JSON in requests
- JWT Validation – Validate a JWT token
- OAuth 2.0 Token Introspection – Allows only authorised traffic with a valid OAuth token
- Rate Limiting – Restricts traffic from a source if too many requests are made within a specific timeframe
- Custom Policies – Develop custom policies using Rust, publish them to Anypoint Exchange and then apply in either API Manager in Connected Mode or YAML configuration file in Local Mode
- And more
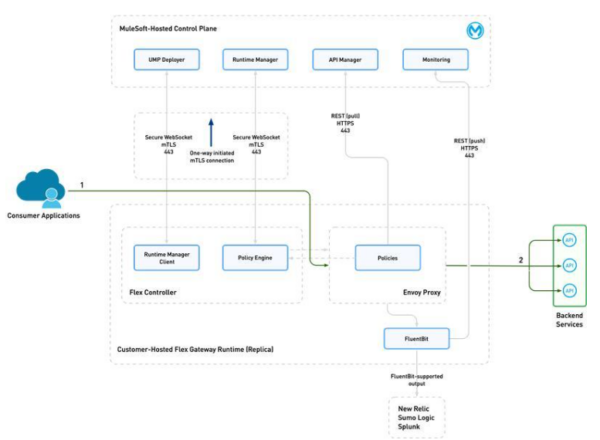
Figure 3: Overview of Flex Gateway’s
Connected mode vs. Local mode – which is right for you
Connected mode
Connected mode offers the advantage of enabling the Anypoint Platform’s control plane to manage Flex Gateway for complete management, observability, and security. Additionally, it provides Anypoint’s API Manager Web UI to simplify API management tasks. In this mode, the Flex Gateway can also be managed through the API Manager API or by directly using the Flex Gateway CLI. This allows for seamless updates to the configuration of the Flex Gateway.
Connected Mode Benefits:
- Centralized Management: Flex Gateway is managed by Anypoint’s control plane
- Anypoint API Manager: Setup your APIs and assign policies using the Anypoint Platform UI
- Enhanced Visibility: Out of the box insights and analytics available on the Anypoint Platform UI
Local Mode
In Local mode, Flex Gateway runs completely disconnected from the Anypoint Platform control plane and is instead managed locally using declarative config files and the Flex Gateway CLI. Local mode is ideal if you have specific requirements where control of Flex Gateway needs to be isolated from the internet. Use a CI/CD pipeline to deploy changes to the Flex Gateways’ configuration files.
Local Mode Benefits:
- Independent: Flex Gateway run autonomously without relying on external services such as the Anypoint Platform
- Offline Functionality: Process requests without needing to connect to any online services
- Isolated Management: Manage Flex Gateway in isolation from the internet
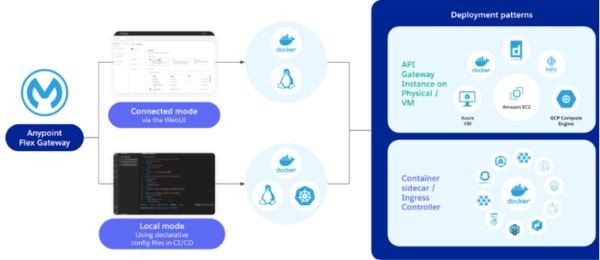
Figure 4: Overview of Connected vs Local Mode
If you take away anything today, let it be this: Don’t let security be an afterthought. By choosing MuleSoft Flex Gateway, you can step into a world where data safety meets blazing speed. Experience how Flex Gateway can transform the security landscape of your applications, irrespective of their architecture.
Ready to elevate your data transit security and enjoy peace of mind? Click here to schedule a free, no-obligation consultation with our Adaptiv experts. Let us guide you through a tailored solution that’s just right for your unique needs. Your journey to robust, reliable, and rapid application security begins now!
FAQ’s
- What is Flex Gateway and its primary use? Flex Gateway is a MuleSoft API gateway designed for managing and securing APIs, offering enterprise-grade security and high performance for applications running anywhere.
- How does Flex Gateway differ from Mule Gateway? Flex Gateway provides a unified way to secure and manage both Mule and non-Mule APIs, bridging the gap in API security and management.
- What are the key benefits of using Flex Gateway? It centralizes proxy management, enforces security policies across APIs, and supports scaling and CI/CD integration for enhanced performance and management efficiency.
- What are the operational modes of Flex Gateway? Flex Gateway operates in connected and local modes, offering flexibility in management either via Anypoint Platform or locally with configuration files and CLI.
- Why is secure data transit important, and how does Flex Gateway facilitate it? Secure data transit is crucial for protecting sensitive information. Flex Gateway ensures this through features like TLS encryption, shared storage for distributed caching, and comprehensive logging and monitoring capabilities.