Organisations are continuously looking for ways to leverage emerging technologies, integrate disparate systems, and streamline their operations. With its Anypoint Platform, integration industry leader MuleSoft provides a potent answer to these problems. DataWeave, an advanced data transformation language that is designed specifically for data transformation to facilitate smooth integration across multiple formats, sits at the core of the MuleSoft runtime.
DataWeave allows businesses to connect legacy systems and third-party applications effortlessly by providing developers with a powerful tool to build integrations. Its versatility in handling data formats such as XML, JSON, and CSV empowers developers to create integrations that are not only efficient but also adaptable to the ever-changing technological landscape. Moreover, DataWeave promotes a systems-agnostic approach, encouraging the reuse of microservices and enhancing maintainability. This capability not only reduces development time but also fosters a more agile and responsive IT environment.
In this blog, we will explore the significance of DataWeave in modern integration strategies, delve into its core functionalities, and uncover advanced features and how they can be applied to potential use cases to benefit your business to easily integrate new and legacy systems.
Why DataWeave is so important
The heart of Mule: Data transformation
At its core, DataWeave is a backbone component of the MuleSoft ecosystem, serving as a powerful data translation language that facilitates seamless interactions between diverse data formats. In an era where data is sourced and distributed to a multitude of various sources — be it web applications, databases, legacy systems, or third-party services — the ability to translate this data efficiently is crucial. DataWeave excels at transforming data from one format to another, enabling organisations to work with the information in a manner that best suits their operational needs. Whether it’s converting XML to JSON or processing CSV files, DataWeave’s robust capabilities ensure that data can be easily collated, manipulated, and utilised across different systems.
Integrate legacy and third-party applications with ease
In many organisations, legacy systems remain vital to daily operations despite their outdated technologies. DataWeave simplifies the integration of these legacy systems with modern applications, bridging the gap between old and new technologies. By offering a straightforward and intuitive syntax for data transformation, DataWeave allows developers to connect disparate systems quickly and efficiently. This ability not only reduces the time and effort required for integrations but also minimises the risk of errors, ensuring that data flows seamlessly across platforms.
Keep systems agnostic to promote reuse of Microservices
As organisations adopt microservices architectures, the need for systems to remain agnostic becomes increasingly important. DataWeave supports this by enabling the creation of reusable services that can handle various data formats without being tightly coupled to any specific technology. This flexibility fosters a more modular approach to development, where services can be repurposed across different projects and teams. By promoting the reuse of microservices, DataWeave helps organisations enhance their overall agility and scalability, allowing them to respond quickly to changing business requirements.
What are DataWeave’s core features?
DataWeave’s power lies in its core functionality, which enables developers to perform a wide range of data transformations with ease. Understanding these fundamental features is essential for leveraging DataWeave effectively in your integration projects. Here, we’ll explore a few useful core features of DataWeave, utilising the DataWeave Playground to show the functionality in action. The DataWeave Playground is a valuable tool provided by MuleSoft that allows developers to develop, validate, and demonstrate data transformations within a browser-based tool withouth the need to setup and run a full application.
For our examples below, let’s assume that the input payload is a collection of Products that each have an ID, SKU, Name, Price, Quantity on Hand, and Category.

Image 1 – Input payload example
Format transformations
One of the most significant features of DataWeave is its ability to perform format transformations seamlessly. Whether you need to convert data from JSON to XML, CSV to JSON, or any other format, DataWeave simplifies the process with its straightforward syntax and powerful built-in functions.
At its simplest form, conversion from one format to another can be achieved by simply setting the output format type in the DataWeave headers.
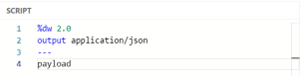
Image 2 – Setting the output format type in the DataWeave headers

Image 3 – Converting xml payload to JSON – Output definition only
As you can see though, the output isn’t a JSON array as we may have wanted but instead is a JSON object. All we require is a simple tweak to the DataWeave to tell it we want to pull out all the “product” nodes into an array.
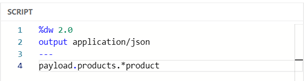
Image 4 – Pull all the product nodes into an array

Image 5 – Converting XML Payload to JSON – Generate Array
From here, we can easily change the output to anything we require by simply changing the output declaration, e.g. CSV or Java array.
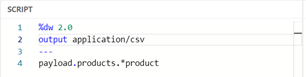
Image 6 – Change output declaration e.g. CSV or Java array

Image 7 – Converting XML Payload to Java
We can even get fancy and output to an Excel spreadsheet with multiple Sheets.

Image 8 – Output to Excel spreadsheet with multiple Sheets

Image 9 – Converting XML Payload to Excel Spreadsheet
Note the output is binary, which when written to a file is a valid Excel document.
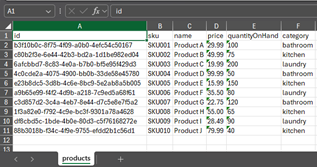
Image 10 – Output Excel file
Converting works in any direction, allowing you to easily transform from any input format to any output format with ease. Whether you’re importing XLSX files and outputting to JSON, importing XML and outputting to CSV, or any permutation of formats, DataWeave does all the heavy lifting for you with minimal developer effort.
Utilising the ‘map’ function for datasets
Ok, so we know that we can quickly and easily transform the data format, but what if we need to transform the data itself?
The ‘map’ function is another cornerstone of DataWeave’s functionality, allowing developers to process arrays or collections of data efficiently. With ‘map’, you can iterate over a dataset, applying a specific transformation to each element, which is particularly useful when dealing with complex data structures.
Back to our example, let’s assume that the JSON schema requires different field names, and an additional field stock value that is the total cost of stock on hand (quantity times price).
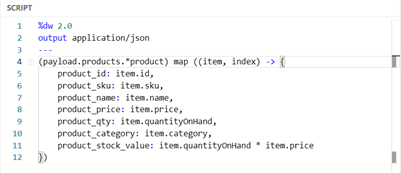
Image 11 – Different fields names, additional field stock value
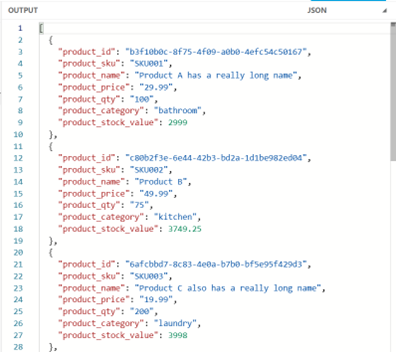
Image 12 – Map object – basic example
Filtering data with the ‘filter’ function
Another powerful feature of DataWeave is the ‘filter’ function, which allows developers to extract specific elements from a dataset based on defined criteria. This functionality is essential when you need to narrow down a collection before applying further transformations or analyses. By using ‘filter’, you can efficiently manage large datasets, ensuring that only the relevant information is processed.
The syntax for the ‘filter’ function is straightforward, taking an array and a condition to evaluate each element. If the condition evaluates to true, the element is included in the output; otherwise, it is excluded.
Going back once again to our Products example, let’s assume that we’re only interested in Products from the ‘kitchen’ category.

Image 13 – Filter products from the ‘kitchen’ category

Image 14 – Filter array – Extract kitchen products
Local functions
DataWeave allows developers to define local functions directly in the header of their scripts, providing a convenient way to encapsulate reusable logic. This feature enhances code organisation and allows you to keep related functionality together, making your transformations more readable and maintainable.
Local functions are defined at the beginning of your DataWeave script, allowing you to specify the function’s name, input parameters, and processing logic. Once defined, these functions can be invoked anywhere within the script, streamlining your transformations and reducing code duplication.
One more time back to our Products example. This time, we want to convert the value fields to a formatted currency String. To do this, we will create a function convertToCurrency in the header, and then pass the relevant values into this function within our mapping.
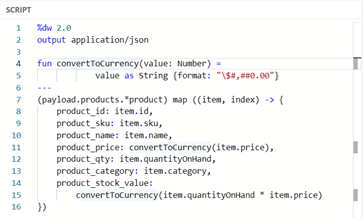
Image 15 – Create a function convertToCurrency in the header
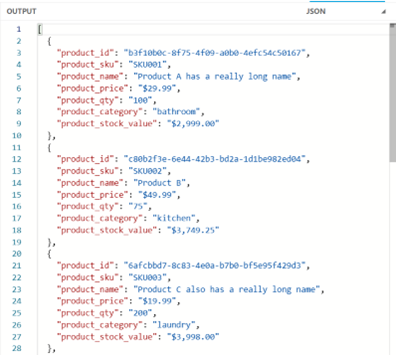
Image 16 – Convert values to Currency String
What are DataWeave’s advanced capabilities?
Once you’ve mastered the core functionalities of DataWeave, it’s time to explore more advanced features that can significantly enhance your data transformations. These features allow for greater flexibility, efficiency, and customisation, empowering developers to tackle complex integration challenges with ease. Here, we’ll delve into several advanced capabilities of DataWeave.
Import modules
MuleSoft provides a catalogue of DataWeave modules that you can import modules functionality from. These libraries provide access to a wide range of built-in functions that can simplify your transformations. By leveraging these libraries, you can enhance your data processing capabilities, making it easier to handle common tasks such as string manipulation, date formatting, and more.
Once again to our Products example. This time, we are reading data from a system that allows Product names that are longer than we can handle. We need to ensure that all the Product names are less than or equal to 15 characters. One of the functions provided in the dw::core:Strings module is withMaxSize which checks that the string length is no larger than the specified maxLength.
To use this function, we declare the import in the header of the DataWeave script, and then apply it as required in our mapping.

Image 17 – Declare the import in the header of the DataWeave script
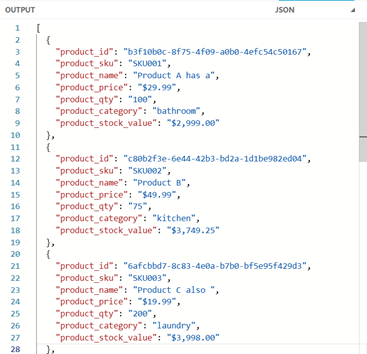
Image 18 – Import withMaxSize function from dw::core::Strings
OK, that example is pretty basic, so how about something a little bit fancier? Let’s now say that we need the category to be the pluralised name. We can import and utilise pluralize from the dw::core::String module
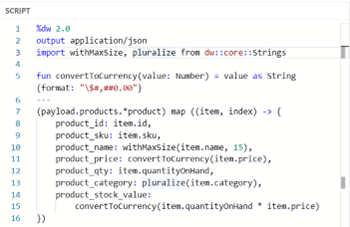
Image 19 – Import and utilise pluralize
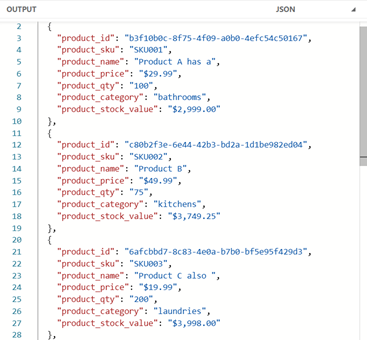
Image 20 – Pluralized categories
Note, that this function does not just add an ‘s’ to the end of the value – “laundry” has been pluralized to “laundries”.
There is a vast catalogue of Modules provided by MuleSoft, covering simple things like String manipulation, through to Cryptography and advanced mathematics. It is worth taking a look at the DataWeave Reference to get an idea of what is available.
Custom modules
We talked earlier about the ability to encapsulate reusable functionality within local functions, and we’ve just seen how we can import functions from Modules. Joining these two features together, DataWeave also enables the creation of custom Modules. Custom Modules allow you to define and package functions that can be invoked multiple times across multiple DataWeave scripts.
Module files do not contain a body, only the header. Let’s create our own Module that contains the convertToCurrency function we defined earlier.
Create a module, myFunctions.dwl, in the Script Explorer
Image 21 – Create a module in the Script Explorer
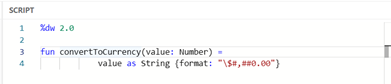
Image 22 – myFunctions.dwl module
We can now import our module the same as we did the MuleSoft modules.
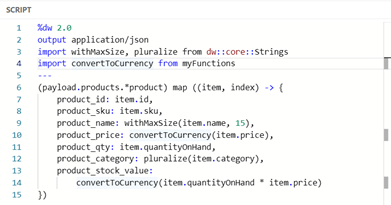
Image 23 – Import module
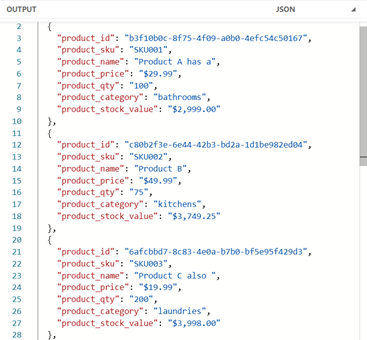
Image 24 – Import module
To replicate this functionality in your own Mulesoft application, create a new file src/main/resources/dataweave/modules/myFunctions.dwl and add our function from earlier.
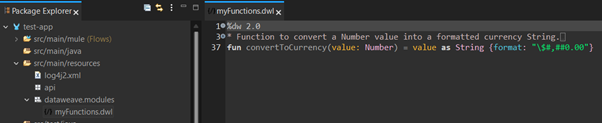
Image 25 – Custom DataWeave Module
When importing from within our project, the lookup path starts at src/main/resources so in our case, the module we will be importing is dataweave::modules::myFunctions
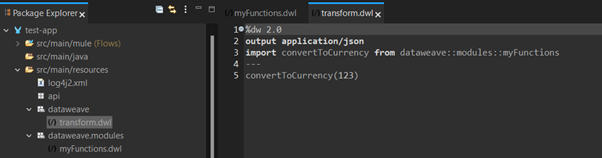
Image 26 – Imported custom module from local file
Overloaded functions
One of the powerful aspects of functions in DataWeave is the ability to overload functions based on input types. This feature allows you to define multiple versions of a function that can handle different data types or numbers of parameters, making your code cleaner and more adaptable.
Just to showcase the functionality, let’s create an overloaded our convertToCurrency function to either:
- Take a Number and return it in currency format; or
- Takes a Number and a Currency Code and return it in currency format with the prepended currency code; or
- Takes a Number and a conversion rate and return the converted value in currency format

Image 27 – Example of an overloaded convertToCurrency function
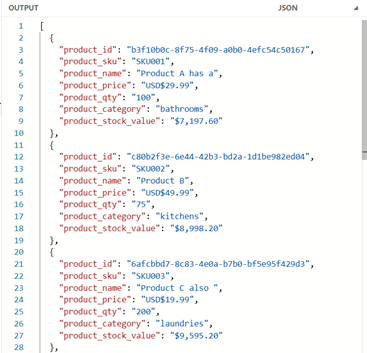
Image 28 – Overloaded convertToCurrency function
Conclusion
As you can see, DataWeave is an essential tool for data transformation within the MuleSoft ecosystem, offering unparalleled versatility and power for integrating diverse data formats. Its ability to perform complex transformations, manage datasets effectively, and support advanced features makes it a vital asset for any organisation looking to enhance their integration capabilities.
I encourage you to explore the rich set of features that DataWeave offers in your integration projects. By leveraging its core functionalities and advanced capabilities, you can streamline your data workflows, improve maintainability, and foster greater agility in your operations.
So why not jump into the official MuleSoft documentation? Explore the comprehensive guides and examples and give it a go for yourself in the DataWeave Playground.